GLORIAD Science and Technology Collaboration Network
Overview
The Global Science and Technology Collaboration Network was initiated in 2005 alongside the GLORIAD project (Global Ring Network for Advanced Applications Development) to enable global collaborative research in large-scale scientific fields such as high-energy physics, astronomy, climate science, and nuclear fusion. The network began with the participation of research networks from 15 countries, including the United States, China, Russia, Canada, and the Netherlands, interconnecting these regions with 10 Gbps capacity.
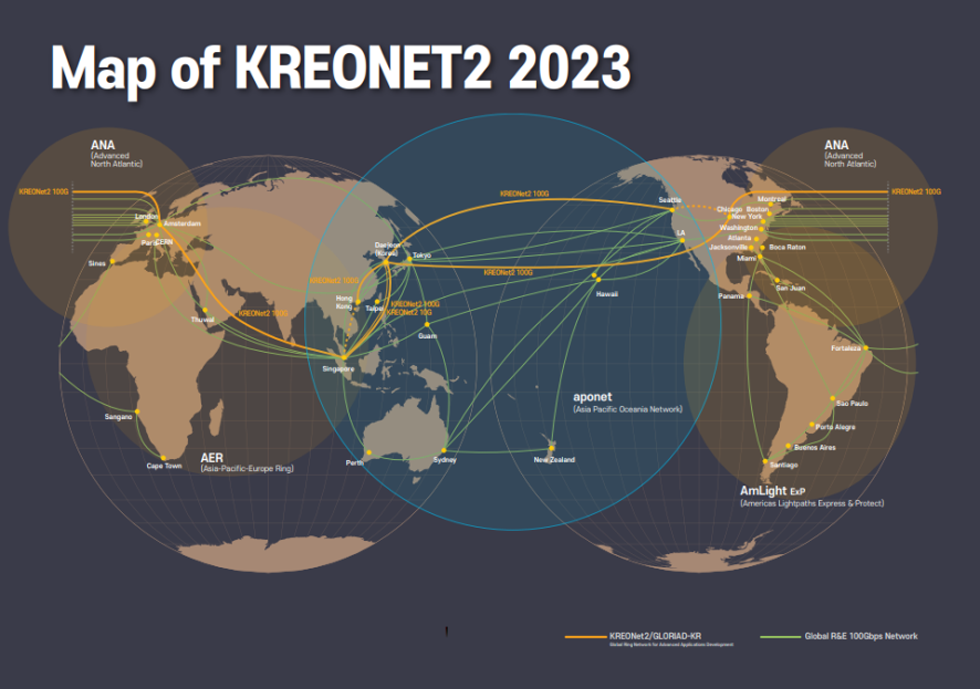
By 2023, the network has evolved into a global 100 Gbps ring, connecting Asia (Daejeon) - North America (Chicago) - Europe (Amsterdam) - Asia (Daejeon), providing an essential backbone for global scientific research collaboration.
Infrastructure
- T100 Gbps International Backbone Lines:
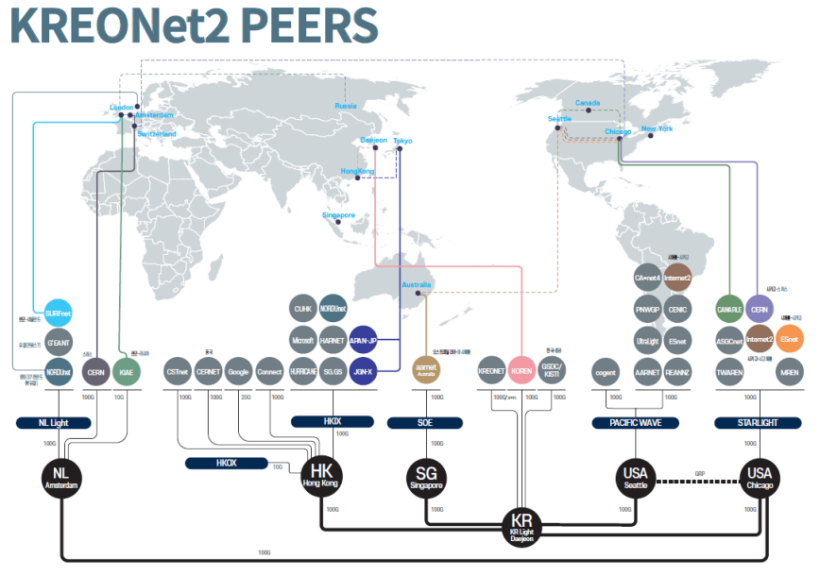
- Hong Kong – Daejeon, Singapore – Daejeon, Daejeon – Chicago, Daejeon – Seattle, Chicago – Amsterdam, Amsterdam – Singapore
- 6 International Points of Presence (PoP):
- Singapore, Hong Kong (China), Daejeon (Korea), Chicago and Seattle (USA), Amsterdam (Netherlands)
- The infrastructure is equipped with optical transmission equipment, high-performance switches/routers, and performance measurement servers to ensure efficient and reliable data transmission across the global network.
This high-speed international backbone supports global scientific collaborations and the exchange of large-scale research data between institutions worldwide.
Key Areas of Support for Large-Scale Scientific Research
1. High-Energy Physics:
- CERN’s Large Hadron Collider (LHC) and High-Luminosity LHC (HL-LHC)
- KEK’s Belle II Experiment in Japan
- Pohang Accelerator Laboratory’s 4th Generation Synchrotron Radiation Accelerator (PAL-XFEL)
- Institute for Basic Science (IBS)’s RAON Heavy Ion Accelerator
2. Nuclear Fusion:
- Korean Superconducting Tokamak Advanced Research (KSTAR)
- nternational Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER)
3. Astronomy and Space Science:
- Korean VLBI Network (KVN)
- Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS)
- Square Kilometer Array (SKA)
- Large Synoptic Survey Telescope (LSST)
- East Asian VLBI Network (EAVN)
- Korea Microlensing Telescope Network (KMTNet) for exoplanet exploration
- Solar and Space Environment Monitoring
4. Climate and Weather Science:
- Research in climate prediction models connected to the National Meteorological Supercomputer
- Atmospheric and oceanic numerical modeling
5. Aerospace:
- National Satellite Ground Network
- Research on the Korean Launch Vehicle (Nuri)
- Operation of satellite tracking stations
- Korea Pathfinder Lunar Orbiter (KPLO) mission
6. Bioinformatics and Genomics:
- International Cancer Genome Consortium (ICGC)
- Pan-Cancer Analysis of Whole Genomes (PCAWG)
- Cancer Genome Regional Data Processing Centers (RDPC)
- National Bio Big Data and Bio Station
7. Overcoming Precision Limits in Space-Time Measurements:
- Contributions to the redefinition of the second through advanced time and space measurement precision techniques.
KREONET’s high-speed network supports these diverse research fields by facilitating the fast transmission of large datasets, enabling cutting-edge discoveries and innovations in collaboration with global scientific institutions.